Within the sector of additive manufacturing of metallic components, inspire is dedicatedly involved in both powder bed processes (Selective Laser Melting, SLM) and powder nozzle processes (Direct Metal Deposition, DMD). This covers all steps of the process chain – from handling the initial powder to the completion of the final component. This enables a comprehensive perspective and optimized implementation of additive manufacturing technologies.
3D Components: Direct Metal Deposition (DMD)
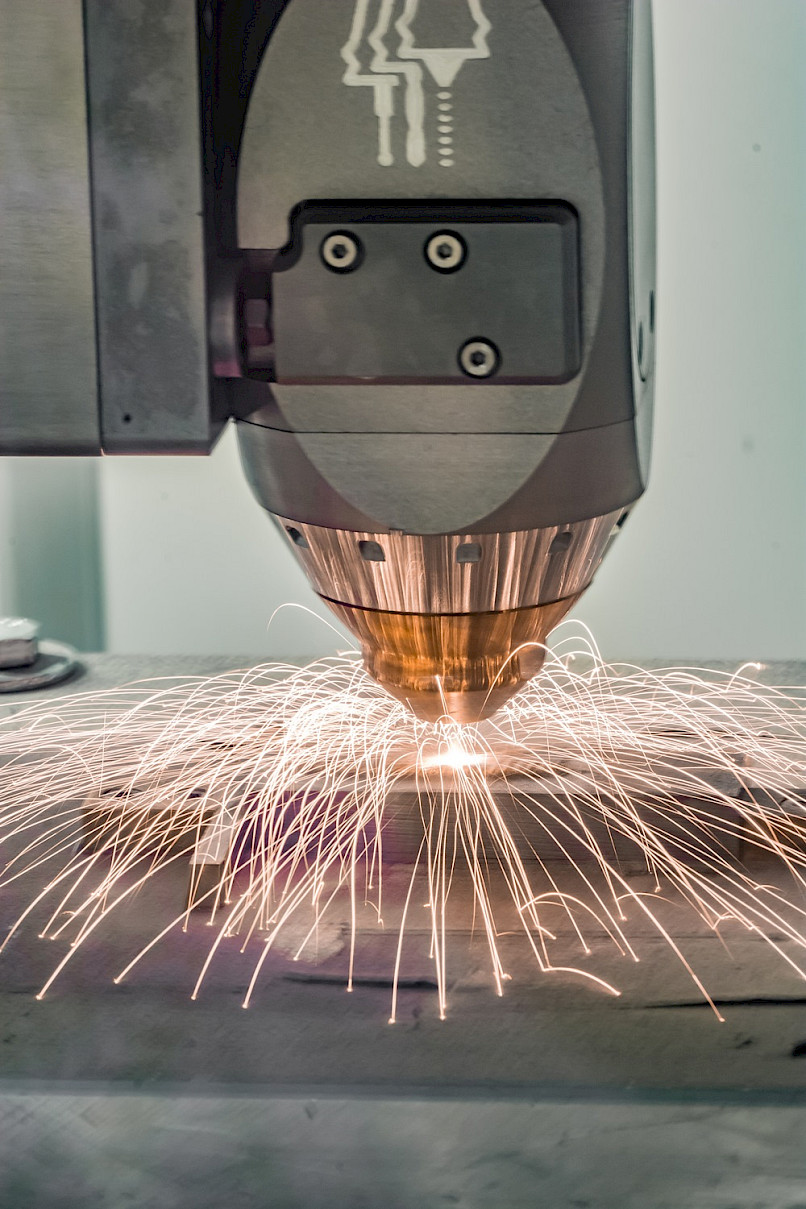

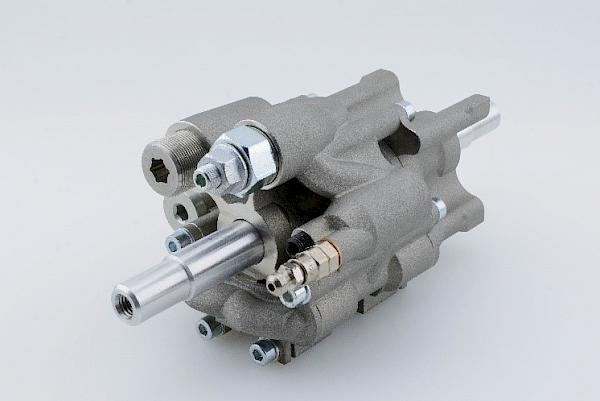
In the additive manufacturing of large metallic components, an modern powder beam process called Direct Metal Deposition (DMD) is utilized. With the aid of this technique, components of significant size, such as turbine blades, kneading hooks, or excavator teeth, can be manufactured both partially and in their entirety. This allows for an extremely precise and flexible production in metal processing.
While the classic laser cladding process is a two-dimensional coating process, laser DMD is a three-dimensional process that can be used to apply a large amount of material within a short period of time. Depending on the type of laser used, build-up rates of approx. 2 kg/h are achieved on the institute's own machine.
In the field of laser cladding, experience is available in process modelling with which the build-up behaviour of the protective layer can be calculated in advance as a function of various machine and laser parameters. The aim is to find a more fundamental understanding of the process and to reduce the time-consuming search for suitable process windows. This is to be transferred to the DMD process in the next few years.
Coatings: Laser Cladding (LC) and High-Speed Laser Cladding (HSLC)
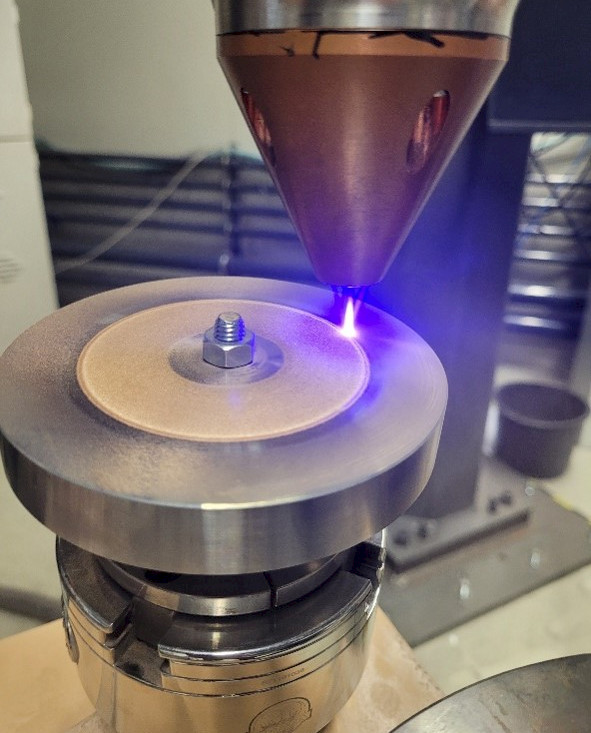
In classical Laser Cladding, coatings are applied directly onto a substrate. The coating can serve various purposes, including wear-resistant layers with integrated abrasive particles (such as ceramics) or tribological layers (like bronze). This technique finds widespread use in various fields, such as brake discs, turbine blades, tools, and bearings.
The main objective of the LC/HSLC (Laser Cladding / High-Speed Laser Cladding) processes is to apply extremely thin protective coatings while aiming to minimize mixing with the base material. Simultaneously, the aim is to create the possibility of joining different materials, even those that are naturally difficult to bond together (such as steel and bronze).
In the case of High-Speed Laser Cladding, the material used is melted before being deposited onto the substrate. This has the advantage of reducing the heat impact on the base material. Consequently, the deposition rate can be significantly increased by a factor of 5 to 10. This increase not only allows for more efficient layer formation but also opens the possibility of fusing diverse materials together.
The application of a blue laser enables a reliable processing of non-ferrous metals. This approach further enhances the versatility of the process.